Imagine a world where the hallways of colleges and universities rang with laughter instead of hushed whispers of worry. Picture a place where students approached their exams and presentations with confidence, instead of being crippled by anxiety. In this thriving academic environment, every learner would have the tools and support they need to thrive, both academically and mentally.
In this article, we will delve into the pressing issue of anxiety in colleges and universities, shining a light on this prevalent and often overlooked problem. We will examine the various factors causing anxiety among students, from the intense academic pressure to the challenges of personal and social adjustments. Moreover, we will explore the detrimental impact anxiety can have on educational outcomes and overall well-being. Fear not, for within these virtual pages, we will guide you through evidence-based strategies and resources aimed at addressing anxiety in higher education institutions. With our expert insights and practical advice, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of anxiety’s effects on students and discover effective approaches to support their mental well-being. Together, let’s create an educational landscape that fosters growth, resilience, and success for every student.

Understanding Anxiety in College Students
The Nature of Anxiety
Anxiety is a common and natural emotional response experienced by individuals in certain situations. It is characterized by feelings of apprehension, worry, and fear. While mild levels of anxiety can be normal and even beneficial, excessive and persistent anxiety can significantly impact a person’s daily life and overall well-being. In college students, anxiety can manifest in various ways and can have a profound impact on their academic performance and overall mental health.
Prevalence of Anxiety in College Students
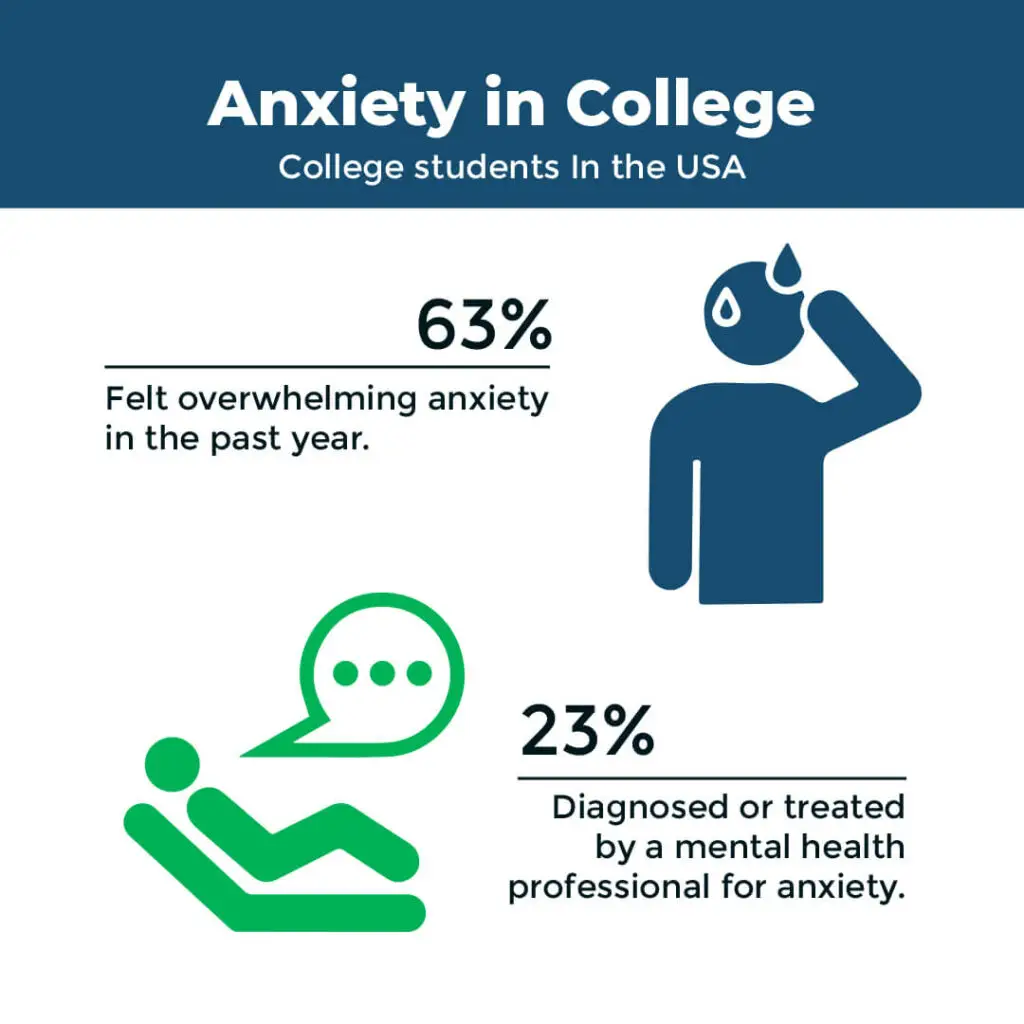
Anxiety disorders are among the most prevalent mental health conditions affecting college students. According to recent studies, approximately 41% of college students worldwide experience symptoms of anxiety at some point during their college years. This high prevalence underscores the need for colleges and universities to prioritize mental health support and resources to address this issue effectively.
Impact of Anxiety on Academic Performance
Anxiety can significantly impair a college student’s academic performance. The constant worry, fear, and nervousness associated with anxiety can make it challenging for students to concentrate, focus, and retain information. Ongoing anxiety can lead to decreased motivation, poor time management, and difficulty completing assignments or studying for exams. Moreover, anxiety can also contribute to insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns, further exacerbating academic challenges. It is crucial for colleges to recognize the detrimental impact anxiety can have on students’ academic success and take proactive steps to support their well-being.
Recognizing Anxiety Symptoms
Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
Physical symptoms are often the most noticeable signs of anxiety. These may include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest tightness, trembling or shaking, sweating, nausea, headaches, and dizziness. Students experiencing these physical symptoms regularly might not immediately attribute them to anxiety, but recognizing and understanding these signs is essential in identifying anxiety in oneself or others.
Emotional Symptoms of Anxiety
Emotional symptoms of anxiety may manifest as excessive worry, fear, irritability, restlessness, feeling on edge or constantly tense, and having difficulty controlling emotions. Students with anxiety might also experience a sense of impending doom or a feeling of being overwhelmed by everyday tasks and responsibilities. Emotional symptoms can significantly impact a student’s overall well-being and daily functioning.
Cognitive Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety can also affect a student’s cognitive abilities. Common cognitive symptoms may include difficulty concentrating, racing thoughts, experiencing mental blocks, having memory problems, and experiencing a constant sense of worry or unease. These cognitive symptoms can cause significant distress for college students, making it challenging to complete assignments, participate in class discussions, or perform well in exams.

Triggers of Anxiety in College
Academic Stress
The demands of college-level coursework, exams, and assignments can place immense pressure on students, leading to increased levels of anxiety. The fear of not meeting academic expectations, maintaining high grades, and the competitiveness of academic environments can contribute to heightened stress levels and anxiety among college students.
Social Pressures
College is a time of significant social transition, where students encounter new social circles, establish friendships, and navigate romantic relationships. However, these social pressures can also trigger anxiety, especially for students who may feel socially isolated or struggle with social interactions. The fear of judgement, rejection, and fitting in can all contribute to increased anxiety levels.
Financial Stress
Financial concerns can be a significant source of anxiety for college students. Tuition fees, textbooks, living expenses, and the prospect of student loan debt can weigh heavily on students’ minds. The financial strain, combined with the pressure to succeed academically, can lead to heightened anxiety levels and affect a student’s overall well-being.
Transition and Change
The transition from high school to college can be a daunting experience for many students, as it often involves leaving home, adjusting to new routines, and navigating unfamiliar environments. These changes can trigger anxiety, as students adapt to a new academic workload, make new friends, and establish independence. The uncertainty and fear associated with this transition can contribute to heightened anxiety levels among college students.
High-Risk Groups for Anxiety
First-Year Students
First-year students are particularly vulnerable to experiencing anxiety as they navigate the challenges of transitioning to college life. The unfamiliarity of the campus, academic expectations, and social pressures can all contribute to heightened anxiety levels. It is vital for colleges to provide adequate support and resources specifically tailored to first-year students to address their unique needs.
International Students
International students face additional stressors and challenges when immersing themselves in a new culture and academic environment. Language barriers, homesickness, cultural adjustments, and the pressure to succeed academically can significantly impact their mental health. Colleges must provide comprehensive support services to help international students manage their anxiety and navigate their college experience successfully.
Students with Pre-existing Mental Health Conditions
Students with pre-existing mental health conditions, such as depression or generalized anxiety disorder, are at a higher risk of experiencing heightened anxiety in a college setting. The added stressors of academic demands, social pressures, and the transition to new surroundings can exacerbate their symptoms. It is crucial for colleges to coordinate with mental health professionals to ensure these students receive appropriate care and support.

Impact of Anxiety on Mental Health
Comorbidity with Other Mental Health Conditions
Anxiety often coexists with other mental health conditions, including depression, substance abuse disorders, and eating disorders. The presence of these conditions can complicate the management and treatment of anxiety. It is essential for colleges to provide integrated mental health services that address the needs of students with comorbid conditions to promote holistic well-being.
Anxiety as a Risk Factor for Suicide
Anxiety, particularly when left unaddressed, can increase the risk of suicidal ideation and self-harm among college students. The constant distress, overwhelming worry, and feelings of hopelessness associated with anxiety can become unbearable for some individuals. Colleges must prioritize suicide prevention initiatives and ensure students have access to timely mental health support.
Impact on Quality of Life and Emotional Well-being
Anxiety can significantly impact a student’s quality of life and emotional well-being. Students with anxiety often report reduced enjoyment in activities they once found pleasurable, strained relationships, and a diminished sense of self-esteem. Managing anxiety effectively is crucial for students to thrive academically and maintain a healthy overall well-being.
How Universities Address Anxiety
Mental Health Services and Supports
Universities must establish comprehensive mental health services and supports to address the needs of students with anxiety. These services may include individual counseling, group therapy, crisis intervention, and psychiatric consultations. Additionally, colleges should promote awareness of on-campus mental health resources and encourage students to seek help when needed.
Academic Accommodations
Recognizing that anxiety can impact a student’s academic performance, universities should provide academic accommodations to support students with anxiety-related challenges. These accommodations may include extended deadlines, flexibility in attendance, and alternative testing arrangements. By implementing such accommodations, colleges can ensure that students with anxiety can fully participate and succeed academically.
Well-being Programs
Incorporating well-being programs into campus life can help reduce anxiety levels among college students. These programs may include mindfulness workshops, stress management courses, yoga and meditation sessions, and recreational activities. By promoting a culture of self-care, colleges can empower students to prioritize their mental health and adopt healthy coping strategies.
Effective Evidence-Based Therapies for Anxiety
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective treatment modality for anxiety disorders. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies. Colleges should offer CBT-based counseling services to students, ensuring they have access to evidence-based therapy options.
Mindfulness-Based Therapies
Mindfulness-based therapies, such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) and Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), have shown promising results in reducing anxiety symptoms. These therapies focus on cultivating present-moment awareness and developing non-judgmental acceptance. Universities should consider integrating mindfulness practices into their mental health services to help students manage anxiety effectively.
Pharmacological Treatments
In some cases, pharmacological treatments may be necessary to manage severe and persistent anxiety. Antidepressant and anti-anxiety medications can be prescribed by healthcare professionals to alleviate anxiety symptoms. However, such treatments should be overseen by medical professionals and integrated with other therapeutic interventions for optimal outcomes.
The Role of College Staff in Addressing Anxiety
Educating Staff about Mental Health
Colleges must prioritize mental health education and training for faculty and staff. Equipping staff with knowledge about common anxiety symptoms, intervention strategies, and available resources enables them to identify and support students experiencing anxiety effectively. This education can create a nurturing environment that promotes overall student well-being.
Providing Teacher Training on Anxiety
Providing training to educators on recognizing and supporting students with anxiety is crucial. Teachers who understand the impact of anxiety on academic performance can create a supportive classroom environment that accommodates the needs of anxious students. By fostering an inclusive and understanding atmosphere, educators can significantly contribute to reducing anxiety levels among students.
Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
Colleges should actively work towards creating a learning environment that promotes positive mental health and supports students with anxiety. This can involve initiatives such as promoting open communication, establishing mental health support groups, and integrating mental health resources into the curriculum. By normalizing discussions about mental health, colleges can reduce stigma and encourage students to seek help when needed.

Implementing Preventative Measures
Peer Support Groups
Peer support groups can play a crucial role in preventing and managing anxiety. These groups provide a safe space for students to share their experiences, seek advice, and provide support to one another. Colleges should establish and promote peer support programs to foster connections and resilience among students.
Stress Management Workshops
Stress management workshops can equip students with practical tools and strategies to cope with anxiety. These workshops may focus on relaxation techniques, time management skills, and healthy coping mechanisms. By providing students with the necessary skills to manage stress effectively, colleges can empower them to tackle anxiety head-on.
Mental Health Education and Awareness Campaigns
Colleges should actively promote mental health education and awareness on campus. This can involve hosting workshops, events, and awareness campaigns that educate students about anxiety, destigmatize mental health, and provide information on available resources. By increasing mental health literacy, colleges can create a supportive environment that encourages early intervention and reduces anxiety levels among students.
Future Directions in Addressing Anxiety in Colleges
Improving Access to Mental Health Services
Colleges must continue to prioritize improving access to mental health services. This includes hiring additional mental health professionals, reducing wait times for appointments, and expanding the range of mental health services available on campus. By ensuring timely access to care, colleges can better support students experiencing anxiety.
Integrating Mental Health Education into Curriculums
Integrating mental health education into curriculums is essential in raising awareness and reducing stigma surrounding anxiety. Colleges should consider incorporating mental health topics into existing courses across disciplines, thereby normalizing discussions about mental health and equipping students with valuable knowledge.
Promoting Student Well-Being as Part of Institutional Culture
To effectively address anxiety in colleges, promoting student well-being must become an integral part of the institutional culture. This involves fostering an environment that prioritizes mental health, encourages help-seeking behaviors, and values the overall well-being of students. By embedding student well-being into the fabric of the institution, colleges can create a supportive and nurturing environment for all students.
In conclusion, anxiety is a prevalent and impactful issue among college students. It can significantly affect academic performance, mental health, and overall well-being. Understanding the nature of anxiety, recognizing its symptoms, identifying triggers, and implementing effective strategies to address it are crucial for colleges and universities. By prioritizing mental health services, providing support and accommodations, and fostering a supportive learning environment, colleges can make a positive impact on the lives of their students and promote their overall well-being.