A recent report from Western University’s faculty of education has shed light on the potential harm of excessive screen time on children’s mental health. The study, which collected data from over 200 Canadian families during the pandemic, found that children who spent more time on screens were more likely to exhibit symptoms of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, the research highlighted the role of parental stress, revealing that children with highly stressed parents were more prone to anxiety and depression if they spent more time on screens. With the significant increase in screen use during the pandemic, it is crucial for parents to be aware of the impact and take steps to modify their children’s screen time habits. This article explores the findings of the study and provides recommendations for parents about managing screen time effectively.
Understanding Screen Time and Children
Screen time refers to the amount of time spent using electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and televisions. It has become an integral part of our daily lives, including those of children. However, it is important to understand the implications of excessive screen time on children’s well-being. By examining the definition of screen time and exploring examples of screen time activities, as well as variations in screen usage across age groups, we can gain insight into its impact on children.
Definition of screen time
Screen time is typically defined as the period spent using electronic devices. This includes activities such as watching TV shows or movies, playing video games, using social media platforms, and browsing the internet. It is important to note that screen time can be both recreational and educational, depending on the content and purpose of the activity.
Examples of screen time activities
Screen time activities can vary greatly and may encompass a wide range of experiences. Some examples include watching cartoons or movies, playing interactive video games, participating in virtual classrooms, engaging with educational apps, and socializing on social media platforms. These activities can provide entertainment, education, and social interaction for children.
Variations in screen usage across age groups
Screen usage patterns tend to differ across different age groups. Younger children, especially those under the age of two, may have limited exposure to screens, as recommended by pediatric guidelines. As children grow older, their screen usage typically increases, as they engage in activities such as online learning, social media interactions, and video streaming. Understanding these variations in screen usage is crucial for developing appropriate guidelines and recommendations for different age groups.
The Impact of Excessive Screen Time on Children’s Mental Health
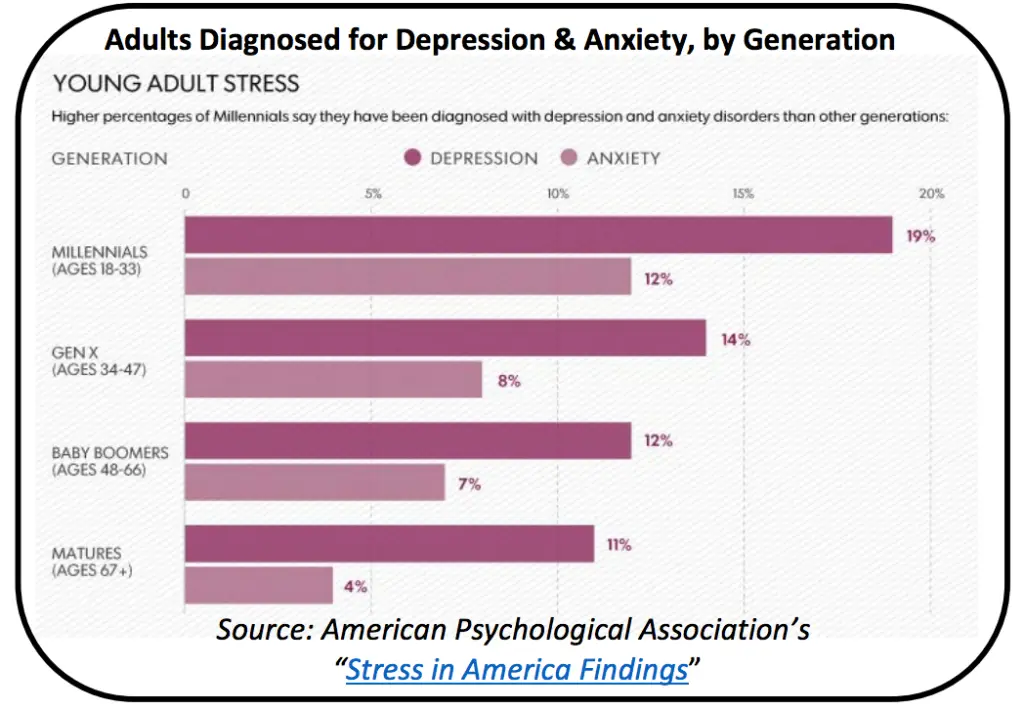
Excessive screen time has been linked to various mental health concerns in children. Research has demonstrated the potential links between prolonged screen time and anxiety, depression, and stress induction in children.
Link between prolonged screen time and anxiety
Studies have shown that children who spend more time on screens are more likely to experience symptoms of anxiety. Excessive screen time can contribute to heightened stress levels, social comparison, and exposure to potentially distressing content. It is important for parents and caregivers to monitor and regulate screen time to minimize the risk of anxiety-related issues.
Link between prolonged screen time and depression
Similarly, prolonged screen time has been associated with higher rates of depression in children. Frequent exposure to negative online content, cyberbullying, and decreased physical activity due to excessive screen use can contribute to depressive symptoms. Creating a balance between screen time and other activities, such as physical exercise and social interactions, is crucial for promoting positive mental health.
The role of screen time in stress induction in children
In addition to anxiety and depression, excessive screen time can also contribute to increased stress levels in children. Continuous exposure to screens, especially in the absence of breaks or relaxation, can overwhelm children’s cognitive and emotional capacities, leading to heightened stress. Implementing screen-free zones and scheduled breaks can help mitigate stress-inducing effects of excessive screen time.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Physical Health Risks Associated with Excessive Screen Time
While the impact of excessive screen time on mental health is well-documented, it is also important to consider the potential physical health risks associated with prolonged screen use. Some key areas of concern include eyesight, sleep patterns, and physical fitness.
Impact on eyesight
Extended periods of screen time can strain the eyes and potentially lead to visual discomfort or vision problems. The blue light emitted from screens can contribute to eye fatigue and digital eye strain. Encouraging children to take regular breaks, practice the 20-20-20 rule (looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes), and maintain proper distance from screens can help protect their eyesight.
Impact on sleep patterns
Excessive screen time, particularly before bedtime, can disrupt children’s sleep patterns. The blue light from screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Screen-free bedrooms and establishing a bedtime routine that includes winding down without screens can promote better sleep quality and duration.
Impact on physical fitness
Spending excessive time on screens can lead to a sedentary lifestyle, which has negative implications for physical fitness. Children who spend more time on screens are likely to engage in less physical activity, leading to potential health issues such as obesity and cardiovascular problems. Encouraging outdoor play, participation in sports or physical activities, and setting screen time limits can promote a healthier lifestyle.
Relation Between Parental Stress and Children’s Screen Time
There is a significant connection between parental stress levels and children’s screen time. The stress experienced by parents can influence children’s screen usage, and in turn, impact their mental health.
The cycle of stress and screen time
Research has shown that stressed parents are more likely to have children who spend more time on screens. During times of increased stress, such as the pandemic, parents may rely on screens as a means of distraction or entertainment for their children. However, excessive screen time can further exacerbate parental stress, creating a cycle of dependence on screens as a coping mechanism.
Impact of parental screen time on children
Children often model their behavior after their parents, and screen time is no exception. If parents excessively use screens in front of their children, it is likely that children will internalize this behavior and engage in similar screen usage habits. Therefore, it is important for parents to be mindful of their own screen time and set appropriate examples for their children.
Parental coping mechanisms and screen time allowance
Parents can adopt healthier coping mechanisms to manage stress, which can reduce their reliance on screens as a distraction tool for their children. Implementing alternative stress management strategies, such as engaging in physical activity, practicing mindfulness, and seeking social support, can help create a more balanced screen time environment for the entire family.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
The Influence of the Pandemic on Screen Time
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted screen time habits, with increased reliance on screens for remote schooling and entertainment. Understanding the effects of the pandemic on screen time is crucial for establishing appropriate guidelines and addressing any enduring impacts.
Increase in screen time during the pandemic
During the pandemic, screen time among children skyrocketed due to the shift towards remote learning and limited social interactions. With schools implementing virtual classrooms and children spending more time at home, screens became essential tools for education and entertainment. However, the sudden increase in screen time raises concerns about its long-term effects on children’s health and well-being.
The necessity of screen time during remote schooling
Remote schooling necessitated the use of screens as a primary mode of communication and education. While this was a necessary adaptation, it is important to acknowledge the potential impact on children’s mental health and physical well-being. Finding a balance between screen-based learning and other activities is crucial for minimizing the negative implications.
The enduring impact of the pandemic on regular screen time habits
Even as restrictions lifted and in-person learning resumed, the enduring impact of the pandemic on screen time habits is evident. Many children continue to rely heavily on screens for entertainment, socialization, and academic purposes. This ongoing reliance emphasizes the need for continued monitoring and management of screen time to ensure a healthy balance between online and offline activities.
Screen Time Recommendations for Different Age Groups
To promote healthy screen time habits, age-appropriate recommendations have been established for children based on their developmental stages. These guidelines take into account the evolving needs and capacities of children as they grow.
Recommendations for children under two
For children under the age of two, it is generally recommended to avoid any screen time, except for video chatting with caring adults. This is because infants and toddlers benefit more from real-world interactions and hands-on experiences for their cognitive, social, and emotional development.
Recommendations for children between two and five
For children between the ages of two and five, it is suggested to limit screen time to less than one hour per day. This time should be spent on high-quality, educational content, and should be accompanied by active engagement and interaction with caregivers.
Recommendations for children over the age of five
For children over the age of five, the recommended screen time is less than two hours per day. It is important to ensure that this time is balanced with other activities, such as physical exercise, social interactions, and outdoor play. Additionally, prioritizing quality screen time, such as educational programs and interactive applications, can enhance the overall benefits for children.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Creating a Balanced Screen Time Environment
To create a balanced screen time environment, it is essential to implement strategies that promote healthy screen habits while ensuring children have opportunities for other activities.
Creating screen-free zones
One effective strategy is to designate specific areas in the home as screen-free zones. This can include bedrooms and mealtime areas, where screens are prohibited. By creating these designated spaces, children have the opportunity to disconnect from screens and engage in other activities, such as reading, playing board games, or having meaningful conversations with family members.
Setting screen time schedules
Setting specific timeframes for screen usage can help establish a routine and reduce excessive or unplanned screen time. By creating a schedule that includes designated screen time slots, children can develop a sense of structure and understand that screen time is a limited resource.
Monitoring child’s screen usage
Regular monitoring of a child’s screen time is crucial for ensuring adherence to established guidelines and promoting accountability. Parents can utilize parental control features built into devices, track usage through apps or software, and engage in open conversations with their children about responsible screen usage. Monitoring also allows parents to identify any potential issues or concerns related to excessive screen time.
The Role of Parents in Modeling Screen Time Behavior
Parents play a critical role in shaping their children’s screen time habits and behaviors. By modeling healthy screen time behavior, parents can positively influence their children’s relationship with screens.
The significance of parent-child screen time
Children observe and imitate the behavior of their parents, making parental screen time habits influential. When parents demonstrate balanced and responsible screen usage, it sets a precedent for their children to follow. Engaging in shared screen activities, such as watching educational content or playing interactive games together, can promote bonding and provide opportunities for discussing appropriate screen time behavior.
Tips for parents to reduce their screen time
To reduce screen time and set a good example for their children, parents can employ various strategies. This may include setting personal screen time limits, designating specific times for digital detox, establishing screen-free activities or hobbies, and practicing mindfulness in daily routines. By prioritizing offline activities, parents can demonstrate the importance of maintaining a healthy balance between screen time and other aspects of life.
Influence of parent screen use on children’s habits
Parental screen time habits have a significant impact on children’s screen usage patterns. If children regularly witness their parents excessively using screens or displaying unhealthy screen behaviors, they are more likely to adopt similar habits. Therefore, it is essential for parents to be intentional and mindful of their own screen time habits to avoid unintentionally influencing their children’s behaviors.

Societal Perception and Public Health Implication of Screen Time
The perception of children’s screen time within society can influence public health implications. By understanding current perceptions and anticipating long-term effects, measures can be taken to address this issue from a public health perspective.
Current public perceptions about children’s screen time
Public perceptions around children’s screen time vary, with differing views on the potential benefits and risks. While some individuals believe that screens are beneficial for educational purposes and entertainment, others express concerns regarding potential negative impacts on children’s health, development, and social interactions. Understanding these varying perspectives can inform public health initiatives and educational campaigns.
Potential long-term public health implications
Excessive screen time during childhood has the potential to lead to long-term health implications. These may include issues such as obesity, musculoskeletal problems, vision impairments, sleep disorders, and mental health disorders. Recognizing the potential long-term consequences of excessive screen time can help inform interventions and policies aimed at promoting healthier screen habits.
Addressing the issue from a public health perspective
Addressing the issue of excessive screen time requires a comprehensive approach from a public health standpoint. This may involve implementing policies and guidelines that promote balanced screen time, educating parents and caregivers about the potential risks and benefits, and fostering partnerships with educational institutions and technology companies to develop responsible screen time practices. Collaboration between various stakeholders is essential for creating a collective societal effort to mitigate the potential harm associated with excessive screen time.
Potential Solutions and Future Directions
To address the challenges posed by excessive screen time, several potential solutions and future directions can be explored.
Emphasizing quality of screen time over quantity
Rather than solely focusing on limiting the quantity of screen time, an emphasis on the quality of screen time can be beneficial. Encouraging children to engage in educational and interactive content, promoting active involvement in screen-based activities, and fostering a critical mindset towards online content can enhance the overall educational and developmental benefits of screen time.
Incorporating screen-free family activities
Incorporating regular screen-free family activities can provide alternatives to screen time and promote bonding among family members. This can include outdoor activities, board games, creative projects, or engaging in shared hobbies. By creating a balance between screen-based and screen-free activities, children can develop a diverse range of skills and interests.
Ongoing research and policy considerations
Continued research is essential for better understanding the long-term effects of screen time on children’s health and well-being. This research can inform evidence-based guidelines and policies that address the evolving needs and challenges associated with screen usage. Ongoing collaboration between researchers, policymakers, healthcare professionals, and technology companies can drive innovation and promote responsible screen time practices.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of screen time on children is crucial in today’s digital age. Excessive screen time can have negative implications for children’s mental and physical health, as well as their overall well-being. By implementing strategies to create a balanced screen time environment, modeling healthy screen time behavior, and addressing the issue from a public health perspective, we can promote responsible and beneficial screen usage for children. Through ongoing research, awareness, and collaboration, we can foster a generation of children who are equipped to navigate the digital world while prioritizing their overall health and well-being.