Are you a nurse struggling with managing anxiety while working? If so, we have just the solution for you. Our product, “Tips for Managing Anxiety While Working as a Nurse,” is designed to provide you with essential strategies and techniques to help cope with anxiety in the demanding field of nursing. With this comprehensive guide, you will learn effective ways to maintain calmness, reduce stress, and improve your overall well-being. Say goodbye to overwhelming feelings and hello to a more peaceful work environment. Let us help you navigate through the challenges of nursing with confidence and tranquility.

This image is property of www.sunbeltstaffing.com.
Understanding the Nature of Nursing and Anxiety
Nursing is a demanding profession that requires compassion, empathy, and the ability to handle high levels of stress. It is no surprise, then, that nurses are often prone to experiencing anxiety. Understanding the nature of nursing and anxiety is crucial for both nurses themselves and those who work alongside them.
Defining Anxiety
Anxiety can be described as a feeling of fear, worry, or unease, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating. It is a normal response to stressful situations, but when it becomes chronic and interferes with daily life, it can be classified as an anxiety disorder.
Why are Nurses Prone to Anxiety?
Nurses are often exposed to high-pressure situations on a regular basis. They work long hours, handle complex medical cases, and are responsible for the well-being of their patients. These factors, combined with the emotional toll of witnessing suffering and dealing with life-or-death decisions, can contribute to increased anxiety levels among nurses.
How Nursing and Anxiety are Interlinked
The nature of nursing itself can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. The constant need to be alert, make quick decisions, and multitask can create a sense of overwhelm and heightened anxiety. Additionally, the emotional connection nurses form with their patients can also contribute to anxiety. The fear of making mistakes or not providing the best possible care can lead to heightened anxiety levels.
Impact of Anxiety on Nurses’ Work Performance
Anxiety can have a significant impact on a nurse’s work performance. It can impair concentration, decision-making abilities, and overall job satisfaction. Nurses experiencing anxiety may struggle to prioritize tasks, communicate effectively with colleagues and patients, and provide the level of care they desire. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize and address anxiety in order to maintain the well-being of both nurses and their patients.
Recognizing Signs of Anxiety
To effectively manage anxiety, it is important to be able to recognize its signs and symptoms. By being aware of these indicators, nurses can take the necessary steps to address their anxiety and seek appropriate support.
Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
Physical symptoms of anxiety can manifest in various ways. Sweating, increased heart rate, shortness of breath, and muscle tension are common physical indicators. Additionally, digestive issues such as stomachaches or nausea, headaches, and fatigue can also be physical manifestations of anxiety.
Emotional Indicators of Anxiety
Anxiety can have a profound impact on a nurse’s emotional well-being. Feelings of restlessness, irritability, and a constant sense of dread are commonly associated with anxiety. Nurses may also experience mood swings, heightened sensitivity, and reduced ability to cope with stress.
Cognitive Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety can impact a nurse’s cognitive abilities, affecting their concentration, memory, and decision-making skills. Nurses experiencing anxiety may find it difficult to stay focused or may struggle to make decisions quickly and effectively. Racing thoughts and an inability to stop worrying about work-related issues are cognitive symptoms that should not be disregarded.
Behavioral Changes That May Indicate Anxiety
Anxiety can also lead to changes in behavior. Nurses who are experiencing anxiety might become more withdrawn, avoid social interactions, or have difficulty interacting with colleagues and patients. They may also have difficulty sleeping, experience changes in appetite, or engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms such as excessive alcohol or substance use.
Common Stressors for Nurses
Understanding the specific stressors that nurses encounter can help shed light on why they are particularly prone to anxiety. By acknowledging and addressing these stressors, nurses can work towards reducing their anxiety levels and maintaining their well-being.
Workload and Shift Patterns
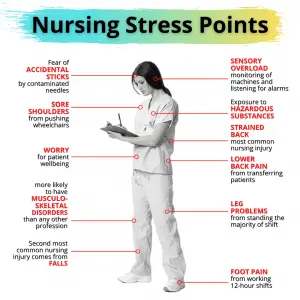
One of the main stressors for nurses is the heavy workload and demanding shift patterns they often face. Long hours, irregular schedules, and the need to constantly be available can lead to increased stress and anxiety levels. The pressure to provide high-quality care while managing multiple tasks and responsibilities can quickly become overwhelming.
Dealing with Difficult Patients and Relatives
Nurses frequently encounter difficult patients or their relatives. This can include patients who are uncooperative, non-compliant, or verbally abusive. Such interactions can be emotionally challenging and can contribute to heightened anxiety levels. Nurses must navigate these difficult situations while maintaining professionalism and providing the best care possible.
Emotional Stress of Patient Care
Nurses form strong emotional connections with their patients. Witnessing suffering, dealing with end-of-life situations, and experiencing loss can take a toll on nurses’ mental and emotional well-being. The emotional stress of patient care can contribute to burnout and heightened anxiety levels among nurses.
Inter-Professional Relations and Team Dynamics
Working in a healthcare team requires effective communication and collaboration. However, conflicts among team members, differences in professional opinions, or a lack of support from colleagues can create stressful work environments. Nurses who feel unsupported or face challenging inter-professional relations may experience increased anxiety as a result.
The Role of the Work Environment in Anxiety
The work environment plays a significant role in contributing to or alleviating anxiety among nurses. Understanding the impact of a stressful work environment and implementing strategies to create a more supportive and positive atmosphere is crucial for maintaining the mental well-being of nurses.
Understanding the Impact of a Stressful Work Environment
A stressful work environment can have detrimental effects on nurses’ mental health. Factors such as a lack of resources, poor leadership, and a high-pressure work culture can contribute to increased anxiety levels. Nurses need a supportive work environment that acknowledges and addresses their needs in order to thrive.
How Management Style Can Affect Anxiety
Management style plays a crucial role in nurses’ well-being and anxiety levels. Supportive and empathetic leaders who actively listen to their employees’ concerns and provide guidance can help alleviate anxiety. On the other hand, authoritative or unsupportive management styles may contribute to increased anxiety levels and overall dissatisfaction among nurses.
The Effect of a Lack of Resources on Anxiety
A lack of resources, such as staffing shortages or insufficient equipment, can significantly impact nurses’ stress levels and contribute to anxiety. Without adequate resources, nurses may feel overwhelmed and unable to provide the quality care they desire. This can intensify anxiety and lead to feelings of frustration and burnout.

This image is property of s3.amazonaws.com.
Self-Care Strategies for Nurses
Taking care of oneself is essential for managing and preventing anxiety. Nurses must prioritize their well-being in order to provide the best care for their patients. Implementing self-care strategies can help nurses reduce anxiety levels and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Importance of Self-Care for Nurses
Self-care refers to activities and practices that promote physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Taking care of oneself is not selfish; it is necessary for nurses to recharge and replenish their energy. Engaging in self-care activities can help reduce stress, alleviate anxiety symptoms, and improve overall mental health.
Nutritional Self-Care Strategies
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining good mental health. Nurses should ensure they eat regular and nutritious meals to support their energy levels and overall well-being. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins will provide the necessary nutrients to fuel the body and mind.
Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is known to have a positive impact on mental health. Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce anxiety levels, improve mood, and increase overall well-being. Nurses should aim to incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise into their daily routine, whether it be through walking, jogging, or participating in fitness classes.
Ensuring Adequate Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for optimal mental health and overall functioning. Nurses often work irregular hours, making it challenging to maintain a consistent sleep schedule. However, prioritizing sleep and creating a sleep-friendly environment can significantly contribute to reducing anxiety levels. Implementing healthy bedtime routines and creating a calm atmosphere in the bedroom are steps nurses can take to promote better sleep.
Mental Health Support for Nurses
Addressing anxiety and seeking appropriate support are essential for nurses’ mental well-being. Nurses should not hesitate to reach out to mental health professionals or utilize available support networks to manage their anxiety effectively.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help
Nurses experiencing chronic anxiety or anxiety disorders should consider seeking professional help. Mental health professionals, such as therapists or psychologists, can provide valuable guidance and support. They can help nurses develop coping mechanisms, navigate challenging situations, and work towards managing their anxiety more effectively.
Approaching Mental Health Professionals
Reaching out to mental health professionals can feel overwhelming for some nurses. However, it is important to keep in mind that mental health professionals are trained to provide support and guidance. It may be helpful to start by researching and finding professionals who specialize in working with healthcare professionals. Open and honest communication will allow mental health professionals to tailor their support to nurses’ unique needs.
Peer Support Groups and Networks
Peer support can be invaluable for nurses experiencing anxiety. Connecting with fellow nurses who share similar experiences can provide a sense of validation and understanding. Peer support groups or networks offer a safe space for nurses to share their struggles, exchange coping strategies, and provide emotional support to one another.
Institutional Support for Mental Health in Nursing
Institutions and healthcare organizations have a responsibility to prioritize the mental health of their nurses. Providing resources such as counseling services, mental health workshops, and access to support networks can have a profound impact on reducing anxiety levels among nurses. Employers should create a culture that destigmatizes mental health issues and actively supports their employees’ well-being.

This image is property of mellowed.com.
Resilience and Coping Strategies
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and effectively cope with challenging situations. Developing resilience is crucial for nurses in managing their anxiety and maintaining their mental well-being.
Building Mental and Emotional Resilience
Building mental and emotional resilience requires self-reflection, self-compassion, and the willingness to learn from difficult experiences. Nurses can cultivate resilience by developing a positive mindset, practicing gratitude, and setting realistic expectations for themselves. Building a support network of colleagues, friends, and family can also bolster resilience.
Effective Nursing Coping Strategies
Nurses benefit from adopting effective coping strategies to manage their anxiety. Engaging in stress-reducing activities outside of work, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or practicing relaxation techniques, can help alleviate anxiety symptoms. Additionally, setting boundaries and prioritizing self-care can contribute to reduced stress levels and increased overall well-being.
Adaptive Vs. Maladaptive Coping Mechanisms
Nurses should be aware of the difference between adaptive and maladaptive coping mechanisms. Adaptive coping mechanisms, such as seeking social support, engaging in self-care, and utilizing relaxation techniques, promote long-term well-being and help manage anxiety effectively. In contrast, maladaptive coping mechanisms, such as excessive alcohol or substance use, avoidance, or rumination, can temporarily alleviate anxiety but ultimately worsen mental health.
Role of Mindfulness in Anxiety Management
Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present in the moment and non-judgmentally observing one’s thoughts and emotions. Incorporating mindfulness techniques into daily routines can help nurses manage their anxiety. Techniques such as mindful breathing, body scans, or guided meditations can promote relaxation, reduce stress, and increase overall well-being.
Incorporating Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can significantly contribute to reducing anxiety levels and promoting overall well-being for nurses. By incorporating these techniques into their routine, nurses can proactively manage their anxiety and improve their mental health.
Practicing Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation techniques can be practiced both inside and outside of work to reduce anxiety. Taking a few minutes each day to sit in a quiet space and focus on the present moment can help calm the mind, reduce stress levels, and promote a sense of inner peace. Mobile applications or online resources can provide guidance for those new to mindfulness and meditation practices.
Benefit of Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet effective relaxation technique that can be used anywhere, anytime. By slowing down the breath and focusing on deep inhales and exhales, nurses can activate the body’s relaxation response and reduce anxiety. Taking short breaks throughout the day to engage in breathing exercises can provide immediate relief from stress and promote mental clarity.
Use of Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and releasing specific muscle groups to promote physical and mental relaxation. By systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups, nurses can release tension and reduce anxiety symptoms. This technique can be particularly beneficial before or after a stressful shift, helping to promote relaxation and minimize the impact of anxiety.
Incorporating Yoga into Your Routine
Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and mindfulness techniques to promote relaxation and overall well-being. Regular practice of yoga can help reduce anxiety levels, improve flexibility and strength, and increase body awareness. Nurses can explore yoga classes or online tutorials to incorporate this holistic practice into their daily routine.
This image is property of bpna.com.au.
Approaching Communication and Relationships at Work
Positive interpersonal relationships and effective communication are vital within any workplace, including the nursing profession. By building strong relationships and fostering open communication, nurses can create a supportive work environment that helps reduce anxiety levels.
Promoting Positive Interpersonal Relationships
Building positive interpersonal relationships with colleagues and patients is essential for nurses’ well-being. Simple acts of kindness, active listening, and offering support to coworkers can foster a positive work environment. Nurses can actively seek opportunities to collaborate and develop relationships, creating a strong support network.
Importance of Effective Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful teamwork and patient care. Clear and honest communication among nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals helps prevent misunderstandings, reduces stress levels, and promotes a sense of collective responsibility. Nurses should actively work on their communication skills, including active listening, empathy, and assertiveness.
Dealing with Difficult Conversations at Work
Difficult conversations are an inevitable part of the nursing profession. Whether it involves addressing conflicts with colleagues or discussing challenging situations with patients or their relatives, nurses need to approach these conversations with empathy and professionalism. By practicing active listening, choosing appropriate language, and seeking common ground, nurses can navigate difficult conversations more effectively, ultimately reducing anxiety.
Building a Supportive Occupational Network
Creating a strong occupational network can provide nurses with a sense of belonging and support. Networking with colleagues, attending professional conferences or workshops, and joining nursing associations can help nurses connect with like-minded individuals and share experiences. A supportive occupational network can offer guidance, validation, and practical advice, making the nursing profession feel less isolating and reducing anxiety levels.
Looking Towards the Future: Preventative Measures
Preventative measures are essential in minimizing anxiety among nurses. By proactively anticipating and planning for stressors and actively seeking personal growth and development, nurses can better navigate the challenges of their profession.
Creating a Healthy Work-Life Balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is crucial for managing anxiety. Nurses must set boundaries between work and personal life to prevent burnout and maintain their mental well-being. Allocating time for hobbies, relaxation, and spending time with loved ones can help create a fulfilling personal life that complements their professional responsibilities.
Anticipatinand Planning for Future Stressors
Nurses should proactively anticipate and plan for future stressors. By identifying potential challenges and developing strategies to navigate them, nurses can reduce anxiety levels. This might involve seeking additional training, preparing emotionally for difficult situations, or learning stress management techniques that can be utilized during challenging times.
Taking Time for Personal Growth and Development
Personal growth and development play a significant role in managing anxiety. Nurses should invest in their own professional and personal development by seeking opportunities for learning, attending workshops, and engaging in reflective practices. By continuously growing and expanding their skill set, nurses can increase their confidence, resilience, and ability to manage anxiety effectively.
The Role of Continued Professional Support
Continued professional support is critical for nurses throughout their careers. Institutions and healthcare organizations should prioritize ongoing education and development opportunities to support nurses’ mental well-being. Regular check-ins, mentorship programs, and access to resources such as counseling services or peer support can provide nurses with the tools and support needed to manage anxiety effectively.
In conclusion, nursing and anxiety are intricately intertwined. Nurses face numerous stressors, both within their work environment and due to the nature of their profession. Recognizing and addressing anxiety is crucial for maintaining the well-being of nurses and allowing them to continue providing high-quality care. By implementing self-care strategies, seeking professional support, and developing resilience, nurses can manage their anxiety and thrive in their profession. With a supportive work environment, effective communication, and the incorporation of relaxation techniques, nurses can navigate the challenges of their profession with a renewed sense of well-being and confidence. Looking towards the future, preventative measures and ongoing professional support are integral to ensuring the long-term mental health of nurses. By prioritizing their own well-being and nurturing personal growth, nurses can not only manage anxiety but also continue to provide exceptional care to their patients.

This image is property of www.freshrn.com.