In this article, you will gain a better understanding of panic disorder and its symptoms. We will explore how panic attacks can affect your daily life and what factors may contribute to its development. Additionally, you will learn about common treatment options available for managing panic disorder. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer picture of what panic disorder is and how it can be effectively addressed.

This image is property of lifelineconnections.org.
What is Panic Disorder?
Panic Disorder is a mental health condition characterized by recurring panic attacks. It is a type of anxiety disorder that involves sudden and intense feelings of fear and apprehension, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heart rate, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and sweating.
Definition of Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder can be defined as a chronic and debilitating condition in which individuals experience recurring panic attacks. A panic attack is a sudden and overwhelming surge of fear or distress that reaches its peak within minutes. These attacks can occur unexpectedly, without any apparent trigger, or in response to specific situations that the person fears or avoids.
Signs and Symptoms of Panic Disorder
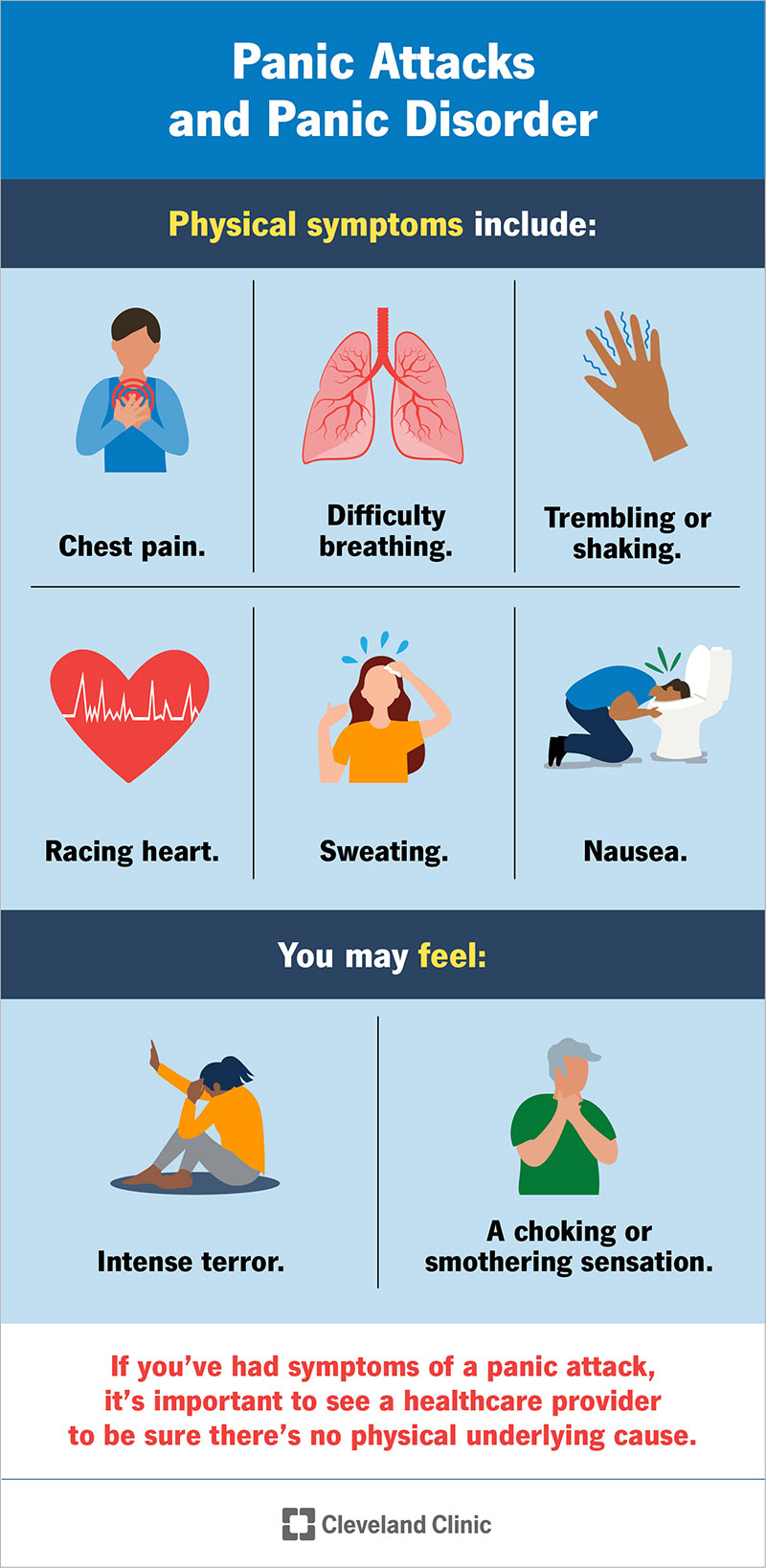
The signs and symptoms of Panic Disorder vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Sudden and intense feelings of fear or terror
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath or a feeling of choking
- Sweating or trembling
- Nausea or stomach discomfort
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Hot or cold flashes
- Fear of losing control or going crazy
- Fear of dying
These symptoms can be extremely distressing and can often lead individuals to avoid certain situations or places for fear of experiencing a panic attack.
Causes of Panic Disorder
The exact cause of Panic Disorder is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and physiological factors. Some possible causes include:
- Family history of Panic Disorder or other anxiety disorders
- Imbalances in brain chemistry, particularly the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine
- History of physical or sexual abuse
- Major life stressors or traumatic events
- Chronic medical conditions, such as heart disease or respiratory disorders
- Substance abuse or withdrawal
While these factors may increase the likelihood of developing Panic Disorder, they do not guarantee its occurrence. It is important to remember that Panic Disorder is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors.
Diagnosing Panic Disorder
Criteria for Diagnosing Panic Disorder
To be diagnosed with Panic Disorder, certain criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) must be met. These criteria include:
- Recurrent unexpected panic attacks that are not caused by a specific situation or substance
- Persistent concern or worry about having additional panic attacks
- Significant behavioral changes related to the panic attacks, such as avoiding certain places or situations
- Exclusion of other medical conditions or substances that may cause similar symptoms
If you consistently experience panic attacks and meet these diagnostic criteria, it is important to seek professional evaluation and diagnosis.
Medical Evaluation for Panic Disorder
When seeking a diagnosis for Panic Disorder, it is essential to undergo a thorough medical evaluation to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be causing or contributing to the panic attacks. A medical professional may conduct physical examinations and order laboratory tests to ensure that there are no other medical explanations for the symptoms experienced.
Differential Diagnosis of Panic Disorder
It is not uncommon for panic attacks to be mistaken for other medical conditions, such as heart attacks or respiratory disorders. This is why a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to differentiate Panic Disorder from other potential causes. A differential diagnosis is crucial in order to provide the appropriate treatment and support for individuals with Panic Disorder.

This image is property of media-engine-production-public.s3.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com.
Types of Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia
Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia refers to when individuals experience panic attacks and also have a fear of being in places or situations where they might have difficulty escaping or receiving help in the event of a panic attack. This fear often leads to avoidance behaviors and can greatly impact an individual’s daily life and functioning.
Panic Disorder without Agoraphobia
Panic Disorder without Agoraphobia refers to when individuals experience panic attacks, but do not have a fear of being in certain places or situations. This form of Panic Disorder may still significantly impact an individual’s life, as they may fear the unpredictability of panic attacks and the distressing symptoms associated with them.
Limited Symptom Panic Attacks
Limited Symptom Panic Attacks are characterized by panic attacks that involve fewer than four physical symptoms. While these attacks may not meet the full criteria for Panic Disorder, they can still cause significant distress and impairment in daily life.
Treating Panic Disorder
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is considered one of the most effective forms of treatment for Panic Disorder. It focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to panic attacks. Through CBT, individuals can learn to reframe their thoughts and develop coping strategies to better manage and reduce the frequency and intensity of panic attacks.
Medications for Panic Disorder
Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines, may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of panic attacks. SSRIs are commonly used in the long-term treatment of Panic Disorder, while benzodiazepines may be used on a short-term basis for acute anxiety relief. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medication regimen for individual needs.
Relaxation Techniques for Panic Disorder
In addition to therapy and medications, learning and practicing relaxation techniques can be beneficial in managing Panic Disorder. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can help individuals calm their minds and bodies during moments of anxiety and panic.
This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.
Managing Panic Disorder in Everyday Life
Creating a Supportive Environment
Having a supportive environment is crucial for individuals with Panic Disorder. This can include having understanding and empathetic friends and family members who can offer emotional support and assistance during times of distress. Educating loved ones about Panic Disorder can help foster a more supportive and understanding environment.
Panic Disorder and Work
Managing Panic Disorder in the workplace can be challenging, but it is possible. It may be beneficial to inform your employer or supervisor about your condition, as they may be able to provide accommodations or support. Utilizing relaxation techniques and seeking therapy during non-work hours can also help manage symptoms and reduce the impact of Panic Disorder on work performance.
Tips for Self-Help in Panic Disorder
There are various self-help strategies that individuals with Panic Disorder can incorporate into their daily lives. These may include:
- Creating a routine and sticking to it
- Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity
- Prioritizing self-care, including maintaining a healthy diet and getting enough sleep
- Avoiding excessive caffeine or stimulant intake, as they can increase anxiety
- Practicing stress-management techniques, such as journaling or creative outlets
These self-help strategies can be complementary to therapy and medication, providing individuals with additional tools for managing Panic Disorder.
Understanding the Impact of Panic Disorder
Effects on Mental Health
Panic Disorder can significantly impact an individual’s mental health and well-being. The constant anxiety and fear of experiencing panic attacks can lead to increased levels of stress and emotional distress. It is not uncommon for individuals with Panic Disorder to develop co-occurring mental health conditions, such as depression or other anxiety disorders, as a result of the ongoing challenges associated with their condition.
Effects on Physical Health
The physical symptoms experienced during panic attacks can take a toll on an individual’s physical health. The increased heart rate, chest pain, and shortness of breath can be physically exhausting, leading to fatigue and reduced functioning in daily life. Additionally, the long-term effects of chronic stress and anxiety on the body can contribute to other physical health conditions.
Influence on Relationships
Panic Disorder can also impact relationships, both romantic and platonic. The unpredictability of panic attacks and the resulting avoidance behaviors can strain relationships, as it may be difficult for loved ones to understand and support individuals with Panic Disorder. Open and honest communication, as well as individual and couples therapy, can help manage the impact of Panic Disorder on relationships.

This image is property of www.bmhsc.org.
Exploring Coping Strategies for Panic Disorder
Breathing Techniques
Deep breathing exercises can be effective in reducing anxiety and panic symptoms. By focusing on slow, deep breaths, individuals can activate the body’s relaxation response and calm their nervous system. Breathing techniques can be practiced at any time, making them a valuable tool for managing panic attacks in various situations.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive Muscle Relaxation involves systematically tensing and then releasing different muscle groups to promote relaxation and reduce tension. This technique helps individuals become more aware of the physical sensations in their bodies and can be helpful in managing the physical symptoms experienced during panic attacks.
Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness Meditation involves focusing attention on the present moment without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can reduce anxiety and stress by redirecting their attention away from negative thoughts and feelings. Mindfulness techniques can be practiced through guided meditations, breathing exercises, or simply paying attention to one’s surroundings and sensations.
Prevention and Early Intervention
Identifying Risk Factors
While it may not be possible to prevent Panic Disorder entirely, identifying and addressing risk factors can help reduce the likelihood of developing the condition. Some potential risk factors include a family history of anxiety disorders, experiencing traumatic or stressful events, or having a history of physical or sexual abuse. By recognizing these risk factors, individuals can work with healthcare professionals to develop strategies for reducing their impact on mental health.
Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the early warning signs of a panic attack can help individuals intervene and manage their symptoms before they escalate. Common early warning signs include increased heart rate, muscle tension, shallow breathing, and heightened feelings of anxiety. By becoming familiar with these signs, individuals can implement coping strategies or seek support to prevent the onset of a full-blown panic attack.
Intervening in Panic Disorder
Early intervention is crucial in managing Panic Disorder. Seeking professional help as soon as symptoms arise can prevent the condition from worsening and improve the long-term prognosis. With the support of trained professionals, individuals can learn effective coping strategies and receive appropriate treatment tailored to their needs.

This image is property of media-engine-production-public.s3.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com.
Seeking Professional Help
Finding the Right Therapist
When seeking professional help for Panic Disorder, it is essential to find a therapist with experience and expertise in treating anxiety disorders. Look for mental health professionals who specialize in cognitive-behavioral therapy or other evidence-based approaches for Panic Disorder. Building a strong therapeutic relationship based on trust and open communication is crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
Choosing the Right Treatment Approach
Each individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another in managing Panic Disorder. It is important to explore different treatment approaches, such as therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Working closely with a healthcare professional, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment plan and adjust it as necessary.
Importance of Psychoeducation
Psychoeducation plays a vital role in managing Panic Disorder. By learning about the condition, its causes, and available treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions and actively participate in their own recovery. Psychoeducation can also help reduce feelings of stigma and shame associated with mental health conditions, allowing individuals to seek the support they need without fear of judgment.
Conclusion
Understanding Panic Disorder is crucial for individuals experiencing this mental health condition. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking professional help, and implementing coping strategies, individuals with Panic Disorder can regain control of their lives and embrace a future beyond their condition. It is important to remember that there is hope and support available, and seeking help is the first step towards a life free from the constraints of Panic Disorder.