Have you ever experienced anxiety symptoms even when you don’t feel anxious? It’s a common experience for many individuals with anxiety disorders. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind these symptoms and how understanding them can help you fully comprehend anxiety disorders. It’s important to consult with your doctor to rule out any medical causes before attributing your symptoms solely to anxiety or stress. There are several factors that can contribute to anxiety symptoms, such as being unaware of your anxious tendencies, hyperstimulation from frequent stress responses, elevated stress levels that feel normal, other sources of stress, underlying factors causing anxiety, side effects of medications, and various other factors. By understanding these reasons, you can begin to take the necessary steps towards managing and reducing your anxiety symptoms effectively.

This image is property of www.verywellmind.com.
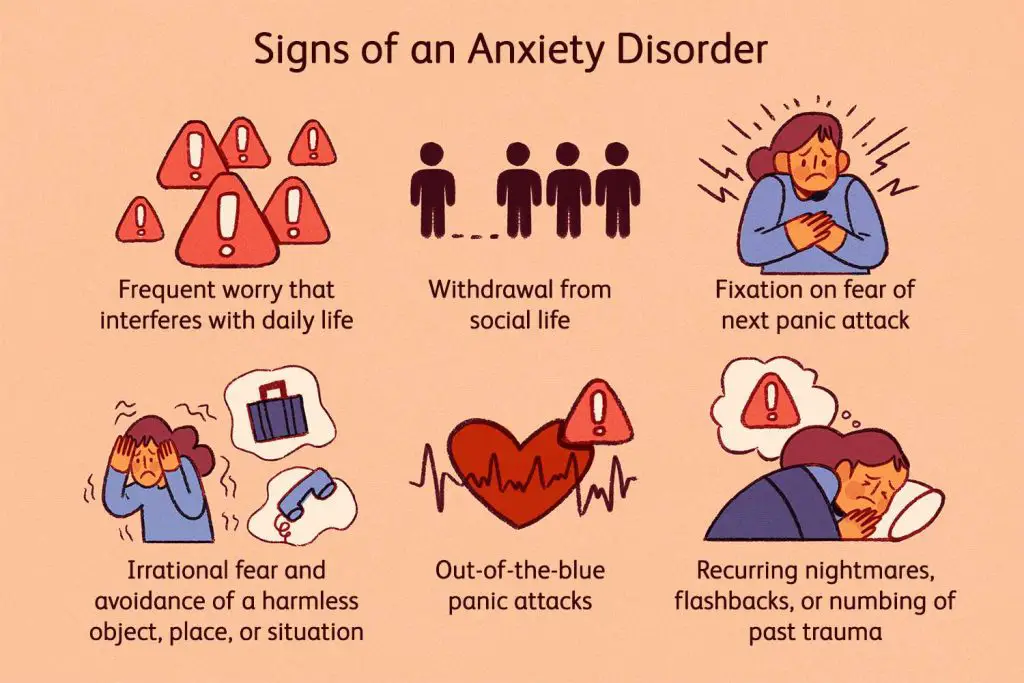
Understanding Anxiety Symptoms
anxiety symptoms are physiological and psychological reactions that occur in individuals who suffer from anxiety disorders. These symptoms can manifest even when a person is not feeling anxious. It is important to understand these symptoms in order to gain a comprehensive understanding of anxiety disorders and find effective ways to alleviate them.
What are anxiety symptoms?
Anxiety symptoms encompass a range of physiological and psychological reactions that are triggered by anxious behavior and activate the body’s stress response. This stress response releases stress hormones into the bloodstream, leading to specific changes in the body to prepare it for a perceived threat or danger. These symptoms are commonly referred to as the stress response, fight or flight response, fight-flight-or-freeze response, or fight-flight-freeze-or-faint response. Examples of anxiety symptoms include increased heart rate, sweating, trembling, and intense feelings of fear or worry.
The physiological reactions linked to anxiety
Anxious behavior can lead to the activation of the body’s stress response, which in turn produces physiological reactions. These reactions are a result of stress hormones being released into the bloodstream. Stress hormones can affect various systems in the body, causing changes such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, heightened alertness, and tense muscles. These reactions are the body’s way of preparing for a potential threat or danger.
The relationship between anxiety symptoms, stress responses, and stress hormones
Anxiety symptoms are closely tied to the body’s stress responses and the release of stress hormones. When a person engages in anxious behavior, it triggers the stress response, leading to the secretion of stress hormones. These hormones then travel to specific locations in the body to bring about the necessary physiological, psychological, and emotional changes. These changes provide the body with an emergency boost of energy and resources to deal with the perceived threat or danger. In turn, these reactions and the stress hormones released contribute to the manifestation of anxiety symptoms.
Root Causes of Anxiety Symptoms When Not Feeling Anxious
There are several reasons why anxiety symptoms can occur even when a person is not feeling anxious. These underlying causes can help explain why the body exhibits anxiety symptoms in the absence of perceived threats or dangers.
Lack of self-awareness about anxiety
Many individuals with anxiety disorders may not be aware that they are anxious. This lack of self-awareness may stem from growing up with anxious behaviors that were perceived as normal or not causing problems. It is common for anxious people to only become aware of their issues with anxiety when they experience unexplained physical symptoms that indicate a problem with anxiety. Recognizing and acknowledging one’s anxious tendencies is an important step towards understanding and managing anxiety symptoms.
Becoming hyperstimulated due to frequent stress responses
When stress responses occur infrequently, the body has the ability to recover relatively quickly. However, if stress responses occur too frequently, such as from ongoing anxious behaviors, the body may not fully recover. Incomplete recovery can leave the body in a state of semi-stress response readiness, leading to hyperstimulation. Hyperstimulation occurs when the body remains in an activated state, even when the stress response has not been triggered. This hyperstimulation can contribute to the manifestation of anxiety symptoms, even in the absence of an actual threat or danger.
Elevated stress levels that feel normal
Anxious people often live with elevated stress levels that have become their normal state. These elevated stress levels may seem normal to them, even though they are above the normal range. Constantly living with elevated stress levels can contribute to the presence of anxiety symptoms, even when a person does not feel anxious in a specific moment. It is essential to recognize and address these elevated stress levels to effectively manage anxiety symptoms.
Other Factors That Could Cause Anxiety Symptoms
In addition to the root causes mentioned above, there are other factors that can contribute to the occurrence of anxiety symptoms, even in the absence of perceived anxiety.
Side effects of certain medications
Some medications, including anti-anxiety and antidepressant medications, can cause side effects that mimic anxiety symptoms. These side effects can include headaches, nausea, diarrhea, dry eyes, dizziness, trembling, and more. If you suspect that your medication may be causing anxiety-like side effects, it is important to discuss this with your doctor or pharmacist to explore potential solutions or alternatives.
Impact of recreational drugs and stimulants
Recreational drugs and stimulants can also contribute to the manifestation of anxiety symptoms. These substances can alter brain chemistry and increase anxiety levels, leading to symptoms such as increased heart rate, restlessness, and heightened stress responses. It is important to understand the potential effects of these substances and make informed decisions regarding their use.
Effects of sleep deprivation, fatigue, and hyperventilation
Sleep deprivation, fatigue, and hyperventilation can all impact the body’s stress levels, potentially leading to anxiety symptoms. Lack of sleep and fatigue can disrupt the body’s natural balance and increase stress hormone levels. Hyperventilation, which is characterized by rapid breathing, can lead to changes in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the body, triggering anxiety-like symptoms. It is important to prioritize adequate sleep, manage fatigue, and practice proper breathing techniques to minimize the occurrence of these symptoms.
Vitiation due to low blood sugar, nutrition deficiency, and hydration
Low blood sugar, nutrition deficiencies, and dehydration can all contribute to feelings of anxiety and the manifestation of anxiety symptoms. These factors can disrupt the body’s proper functioning and lead to imbalances that can trigger anxiety-like reactions. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels, consuming a nutritious diet, and staying adequately hydrated are important for overall well-being and managing anxiety symptoms.
Hormonal changes causing anxiety symptoms
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can also contribute to the occurrence of anxiety symptoms. Fluctuations in hormone levels can affect neurotransmitters and brain chemistry, potentially leading to increased anxiety levels. It is important to be aware of these hormonal changes and their potential impact on anxiety symptoms, seeking appropriate support and management strategies as needed.
Impacts of Underlying Factors of Anxiety
The underlying factors that contribute to anxiety, including early life behaviors and circumstances, can have lasting impacts on an individual’s anxiety levels and the manifestation of anxiety symptoms.
Anxiety caused by early life behaviors and circumstances
Anxiety can often be traced back to early life experiences and behaviors. For individuals who grew up exhibiting anxious behaviors or experiencing traumatic circumstances, anxiety may become a normal part of their lives. These early life factors can shape a person’s perception of stress and anxiety, leading to ongoing issues with anxiety and the associated symptoms. Recognizing the influence of early life factors is crucial for understanding and addressing anxiety.
Misconception of overly stressed bodies as normal
Anxious individuals may mistakenly perceive their chronically stressed bodies as normal. Constantly living with elevated stress levels can create a skewed perspective on what constitutes a healthy baseline. This misconception can lead to a lack of awareness regarding the true underlying causes of anxiety symptoms. Education and self-reflection are important tools for recognizing and challenging this misconception.
Unawareness of the underlying issues causing anxiety
Many individuals with anxiety disorders may not be fully aware of the underlying issues that contribute to their anxiety. These underlying issues can be deeply rooted and may require exploration through therapy, self-reflection, or other forms of support. Without addressing these underlying issues, it can be challenging to effectively manage anxiety symptoms. Developing self-awareness and seeking appropriate guidance and support are crucial steps towards understanding and addressing the underlying causes of anxiety.
This image is property of www.verywellhealth.com.
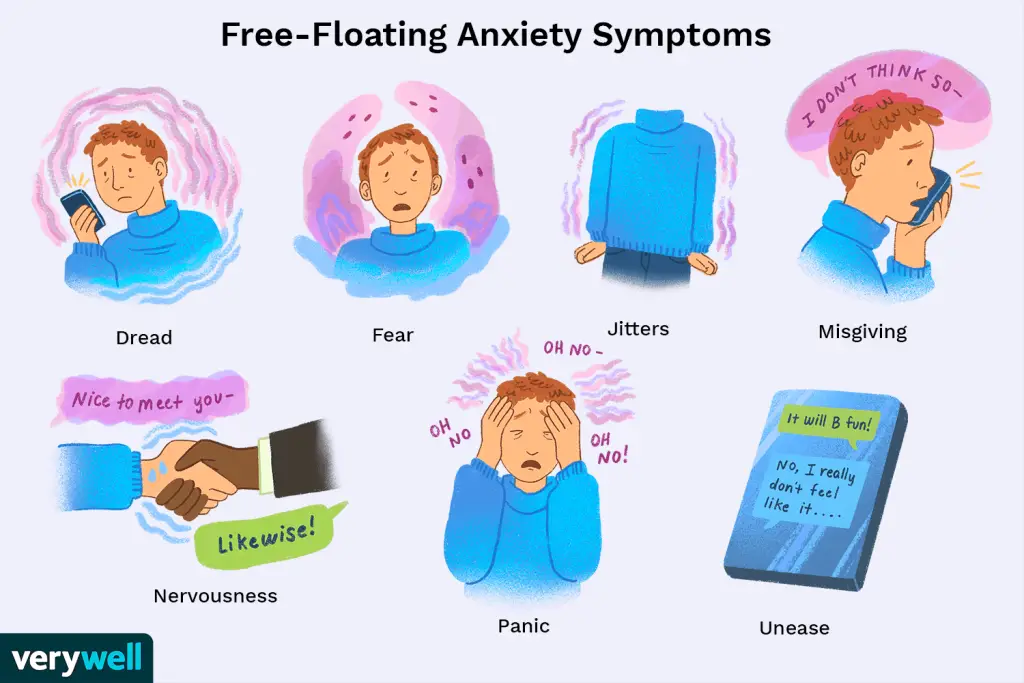
Identification of Anxious People
Recognizing and identifying anxiety in oneself can be a crucial step towards understanding and managing anxiety symptoms. Unexplained physical symptoms can serve as a wake-up call, prompting individuals to acknowledge and address their anxious tendencies.
Realization of being an anxious person due to unexplained physical symptoms
Many people only become aware of their issues with anxiety when they experience unexplained physical symptoms. These symptoms, which may have no apparent cause and cannot be explained by medical conditions or medications, can be a signal that there is an underlying issue with anxiety. Identifying these physical symptoms and recognizing them as potential manifestations of anxiety can provide individuals with the motivation to seek help and address their anxiety symptoms.
Confusion between what is normal and what is caused by anxiety
Anxious individuals may struggle to distinguish between what is considered normal and what is caused by anxiety. Living with chronic stress and anxiety can lead to a skewed perception of what constitutes healthy functioning. This confusion can make it challenging to identify the presence of anxiety symptoms, as anxious behaviors and reactions may be perceived as normal. Education, self-reflection, and seeking professional guidance can help individuals unravel this confusion and gain clarity on the impact of anxiety on their overall well-being.
The Effect of Hyperstimulation
When stress responses occur too frequently or intensely, the body may become stuck in a state of hyperstimulation. This can lead to the manifestation of anxiety symptoms, even when a person is not feeling anxious in a specific moment.
Explaining the dysregulation of the nervous system due to hyperstimulation
Hyperstimulation occurs when the body remains in an activated state, even in the absence of an actual threat or danger. This dysregulation of the nervous system can result from the frequent and intense activation of the body’s stress response. The stress hormones released during these responses can keep the body in a heightened state of arousal, leading to a range of physiological and psychological changes. This dysregulation contributes to the occurrence of anxiety symptoms, as the body remains on high alert, ready to respond to potential threats.
Understanding the recovery time from hyperstimulation
Recovery from hyperstimulation can take a considerable amount of time. The effects of stress on the body can persist long after a stressful event or situation has ended. Research suggests that it can take up to four times longer to recover from the effects of stress than it took to become stressed in the first place. This prolonged recovery period means that the body may continue to exhibit anxiety symptoms, even when a person is not feeling anxious, as it is still in the process of recovering from hyperstimulation.
The role of hyperstimulation in producing anxiety symptoms
Hyperstimulation is a significant factor in the manifestation of anxiety symptoms, even in the absence of anxiety. The overactivation of the stress response and the subsequent release of stress hormones keep the body in a state of heightened arousal. This state can lead to a range of physiological, psychological, and emotional changes that are commonly associated with anxiety symptoms. Recognizing the role of hyperstimulation in anxiety can help individuals understand why they may experience anxiety symptoms, even when they do not feel anxious.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Strategies to Eliminate Anxiety Symptoms
There are various strategies and techniques that can help individuals alleviate and eliminate anxiety symptoms. These approaches focus on addressing the underlying causes of anxiety and promoting overall well-being.
Introduction to surrender sessions
Surrender sessions are designed to create a new relationship with the body and reduce reactivity to anxiety symptoms. Engaging in surrender sessions regularly can provide individuals with deep clarity about their anxiety symptoms, calm a dysregulated nervous system, and shift negative emotional states towards positive ones. Surrender sessions involve letting go of the need to control what the body does and embracing a state of acceptance and relaxation.
Using mapping meditations
Mapping meditations involve consciously shifting the focus from one body part or anxiety symptom to another. This process helps individuals recognize and understand the sensations associated with anxiety symptoms. The act of mapping allows individuals to develop a greater awareness of their physical and emotional experiences, facilitating the identification and management of anxiety symptoms.
Healing hypersensitivity and hypertension
Hypersensitivity refers to an increased sensitivity to stimuli, while hypertension refers to persistently high levels of stress. Healing hypersensitivity and hypertension involves implementing strategies to reduce sensitivity to stimuli and lower stress levels. These may include practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in stress-reducing activities, establishing healthy boundaries, and seeking support from trusted individuals or professionals.
Incorporating emotional reframing
Emotional reframing is a technique that involves communicating directly with the subconscious mind to bring about psychological and physiological shifts. This technique can help individuals reinterpret past experiences and release repressed emotions tied to anxiety. By reframing negative emotions and perceptions, individuals can foster healing and reduce the frequency and intensity of anxiety symptoms.
Use of affirmations for anxiety relief
Affirmations are positive statements that are repeated to foster a shift in mindset and reduce anxiety. By regularly using affirmations, individuals can reprogram their subconscious mind to let go of irrational fears and anxieties. Affirmations can be used during bedtime as a way to promote relaxation and positive thinking.
Role of Medications and Other Sources of Stress
Medications and external sources of stress can contribute to the occurrence of anxiety symptoms, even in individuals who are not feeling anxious.
Understanding the side effects of anti-anxiety and antidepressant medications
Certain medications, including anti-anxiety and antidepressant medications, can produce side effects that mimic anxiety symptoms. These side effects may include headaches, nausea, diarrhea, dry eyes, dizziness, trembling, and brain zaps. It is important to discuss any concerns about medication side effects with healthcare professionals to explore potential dosage adjustments, alternative medications, or discontinuation options, if appropriate.
How external sources of stress can cause anxiety symptoms
Aside from medications, various external sources of stress can contribute to the manifestation of anxiety symptoms. Rigorous physical activity, strenuous exercise, persistent noise, extreme temperatures, sleep deprivation, heavy cognitive load, exciting events, chronic pain, and long study hours are examples of stressors that can stress the body and trigger anxiety-like symptoms. Recognizing and managing these external stressors can help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
This image is property of www.verywellmind.com.
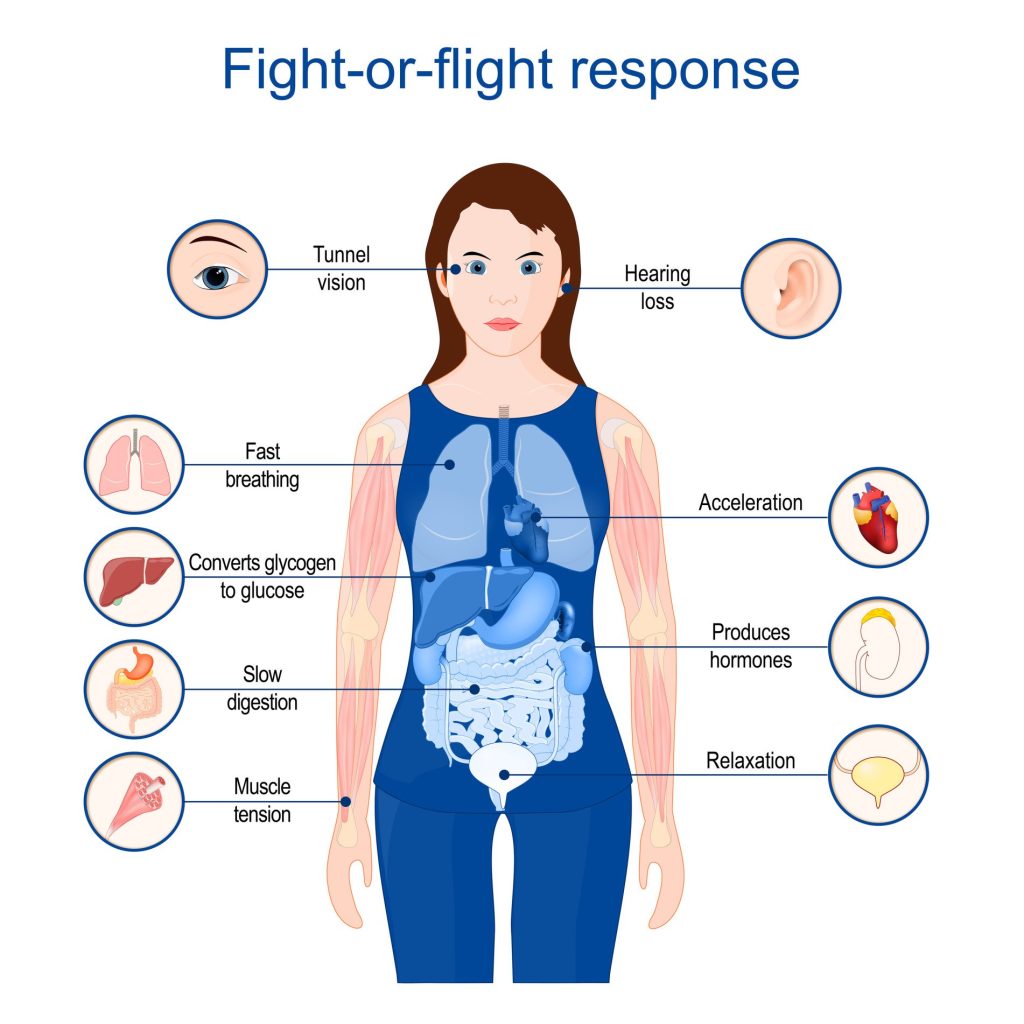
Understanding Stress Responses
Stress responses serve as the body’s natural defense mechanism, triggered in response to perceived threats or dangers.
Different types of stress responses – fight, flight, freeze, or faint
Stress responses can manifest in different ways, commonly referred to as fight, flight, freeze, or faint responses. These range of responses are the body’s way of preparing to confront or escape from a potential threat. The fight response involves a readiness to confront the threat head-on, while the flight response prompts a desire to escape from the threat. The freeze response leads to a state of immobilization, and in some cases, the faint response can cause individuals to lose consciousness when faced with extreme fear or danger.
Explanation of how stress responses stress the body
Stress responses work by activating the body’s stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, which in turn produce physiological changes that prepare the body for action. These changes include increased heart rate, enhanced blood flow to muscles, heightened alertness, and suppression of non-essential bodily functions. While stress responses are essential for survival, chronic or excessive stress can lead to long-term negative effects on the body, including the manifestation of anxiety symptoms.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors
Various lifestyle factors can contribute to the occurrence of anxiety symptoms, even in the absence of anxiety.
How rigorous physical activity and strenuous exercise can cause anxiety symptoms
Engaging in rigorous physical activity and strenuous exercise can lead to the development of anxiety symptoms. These activities put stress on the body, activating the stress response and releasing stress hormones. This physiological response can result in symptoms such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened levels of stress. It is important to engage in physical activity and exercise in a balanced and moderate manner to avoid excessive stress on the body.
The role of persistent noise, temperature extremes, sleep deprivation, etc. in causing anxiety symptoms
Persistent noise, extreme temperatures, sleep deprivation, and other environmental factors can significantly impact anxiety levels and lead to the occurrence of anxiety symptoms. These factors can disrupt the body’s natural functioning and contribute to increased stress hormone production. Implementing strategies to create a calm and conducive environment, prioritizing adequate sleep, and managing external stressors can help minimize the occurrence of anxiety symptoms.
Understanding the various factors that can cause anxiety symptoms when not feeling anxious is essential for effectively managing and alleviating these symptoms. By recognizing the root causes, identifying and addressing underlying issues, and implementing strategies to reduce stress and promote well-being, individuals can take proactive steps towards living a life with reduced anxiety symptoms. Seeking professional support, such as therapy or counseling, can also provide valuable guidance and assistance in navigating the challenges associated with anxiety symptoms. Remember, you are more than anxiety, and there are resources available to support you in your journey towards healing and well-being.
This image is property of www.simplypsychology.org.